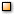
| The research interest of BIG (Behavior/Intervention/Green) Data Laboratory is in discovering new insights by extracting and fitting together implicit, previously unknown and potentially useful pieces of information from big data. It especially focuses on issues at the convergence of engineering and humanities by mining and modeling 'mobile device sensed data' pertaining to human behavior and context, with the goal of identifying and predicting behavior pattern and personal relationship for providing practical insight in business and healthcare. Another research interest is in developing a general statistical framework for effectively and efficiently monitoring, diagnosing, and controlling variation in data-rich environments such as manufacturing and the healthcare and service industries, with the goal of improving process stability and capability for competitiveness for enterprises. The aforementioned research is accomplished with multidisciplinary engineering technologies integrated with data mining, reality mining, statistics, social network analysis, cognitive science, and psychology. The research interests are in : |
|
 |
Business Analytics/Intelligence based on Data Mining and Statistics |
 |
Service Science |
 |
Health/Business Diagnosis |
 |
Health/Business Intervention |
 |
Health/Business Monitoring |
 |
Health/Business Screening |
Specifically, |
|
 |
Smart Healthcare |
 |
Medical Big Data Analysis and Mashup |
 |
Privacy Preserving Remote Medical Service |
 |
Data-Driven Medical Service Science (Service Design and Service Strategy) |
 |
Patient/Process Monitoring and Forecasting |
 |
Hospital Customer Relationship Management (CRM) |
 |
Privacy Preserving Infection Surveillance |
 |
Patient/Customer Behavior Analysis |
 |
 |
 |
--- TERMINOLOGY -- TERMINOLOGY -- TERMINOLOGY -- TERMINOLOGY -- TERMINOLOGY ---
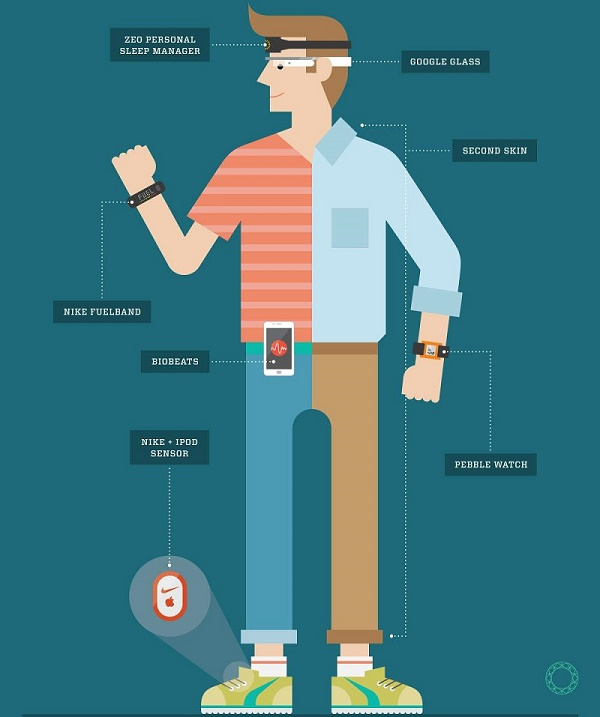
| CRM (Customer Relationship Management) CRM is a philosophy and a business strategy supported by a system and a technology designed to improve human interactions in a business environment. - Paul Greenberg, CRM Magazine, October 2003 |
|
 |
Customers are the most important asset of an organization. There cannot be any business prospects without satisfied customers who remain loyal and develop their relationship with the organization. That is why an organization should plan and employ a clear strategy for treating customers. CRM is the strategy for building, managing, and strengthening loyal and long-lasting customer relationships. CRM should be a customer-centric approach based on customer insight. Its scope should be the "personalized" handling of customers and distinct entities through the identification and understanding of their differentiated needs, preferences, and behaviors. |
|
Data Mining Data mining is the process of automatically discovering useful information in large data repositories. Data mining techniques are deployed to scour large databases in order to find novel and useful patterns that might otherwise remain unknown. They also provide capabilities to predict the outcome of a future observation, such as a predicting whether a newly arrived customer will spend more than $100 at a department store. Data mining is an integral part of knowledge discovery in databases (KDD), which is the overall process of converting raw data into useful information. |
 |
| Data Mining techniques can be used to support a wide range of business intelligence applications such as customer profiling, targeted marketing, workflow management, store layout, and fraud detection. It can also help retailers answer important business questions such as "Who are the most profitable customers?", "What products can be cross-sold or up-sold?" and "What is the revenue outlook of the company for next year?". |
|
|
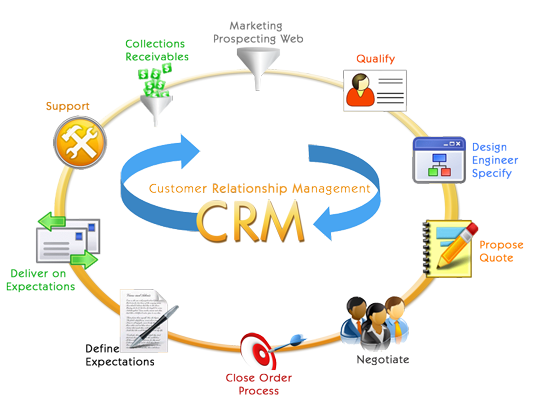
Business Intelligence The competitive forces prevailing in the world of commerce today require firms to operate as efficiently and productively as possible in order to maintain and enhance market share, profitability and shareholder value. An essential element to achieving success involves the continuous enhancement of knowledge and understanding of the business environment by employees at all levels. This is can be accomplished by implementing processes which augment the accessibility and communication of value-added information throughout the organization. |
|
 |
As a result there has been an increased demand for cutting-edge information technology by businesses in all industries. This increased demand has further resulted in an explosion in the development and implementation of technologies that store, retrieve, manipulate, report, analyze and communicate data. The increased availability of value-added information throughout the firm helps to augment the knowledge of the business to a variety of individuals. Decision makers can use information to better devise and implement business strategy based on Economic theory to more effectively manage available resources in order to best meet the needs of the ultimate consumer. The above process has evolved into a philosophy referred to as "business intelligence." |
|
Activity Monitoring Activity monitoring is an automated process that applies operational intelligence and application integration technologies to alert individuals to changes in complex systems that may require action. It includes business activity monitoring, customer churn detection, computer intrusion detection, and network performance monitoring. |
 |
 |
Quality Engineering Quality engineering is the set of operational, managerial, and engineering activities that a company uses to ensure that the quality characteristics of a product are at the nominal or required levels. |
|
Statistical Process Control Statistical process control (SPC) is a powerful collection of problem-solving tools useful in achieving process stability and improving capability through the reduction of variability. |
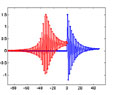 |
|
Statistical Learning Vast amount of data are being generated in many fields, and the statistician's job is to make sense of it all: to extract important patterns and trends, and understand "what the data says." We call this learning from data. The challenges in learning from data have led to a revolution in the statistical sciences. Statistical learning plays a key role in many areas of science, finance, and industry. |
|
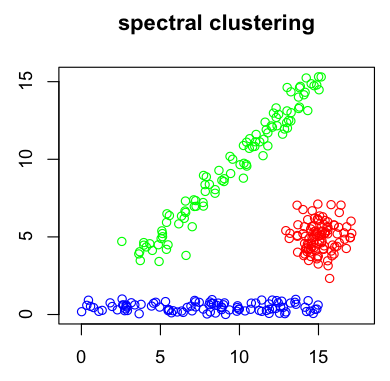 |
Here are some examples of learning problems: 1) Predict whether a patient, hospitalized due to a heart attack, will have a second heart attack. The prediction is to be based on demographic, diet and clinical measurements for that patient. 2) Predict the price of a stock in 6 months from now, on the basis of company performance and economic data. 3) Identify the numbers in a handwritten ZIP code, from a digitized image, 4) Estimate the amount of glucose in the blood of a diabetic person, from the infrared absorption spectrum of that person's blood, 5) Identify the risk factors for prostate cancer, based on clinical and demographic variables. |
|
Multivariate Analysis Scientific inquire is an iterative learning process. Objective pertaining to the explanation of a social or physical phenomenon must be specified and then tested by gathering and analyzing data. In turn, an analysis of the data gathered by experimentation or observation will usually suggest a modified explanation of the phenomenon. Throughout this iterative learning process, variables are often added or deleted from the study. Thus, the complexities of most phenomena require an investigator to collect observations on many different variables. Because the data include simultaneous measurements on many variables, this body of methodology is called multivariate analysis. |
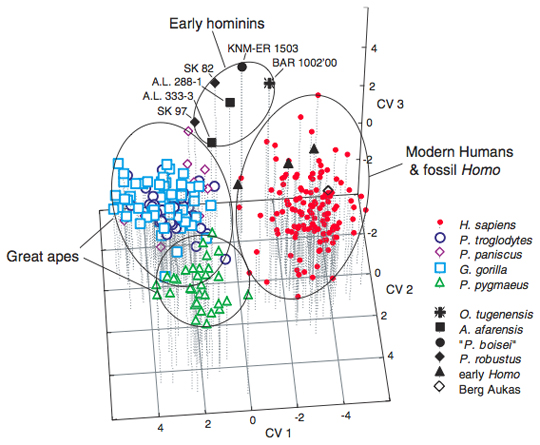 |
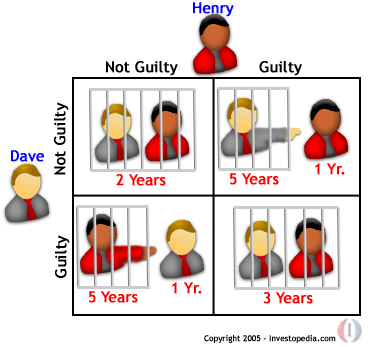 |
Game Theory Game theory is a collection of mathematical tools useful in analyzing the interaction among multiple decision makers competing for conflicting interests. As a critical solution concept to competition, Nash equilibrium represents a combination of all players' decisions in which no player unilaterally augments its interest by changing its own decision specified in the combination. |
|
References:
- Fawcett and Provost (1999), Activity monitoring: noticing interesting changes in behavior, in Proceedings of KDD-99, pp. 53-62. - Hastie, Tibshirani, and Friedman (2001), The Elements of Statistical Learning - Johnson and Wichern (1998), Applied Multivariate Statistical Analysis - Kudyba and Hoptroff (2001), Data Mining and Business Intelligence : A Guide to Productivity - Montegomery (2005), Introduction to Statistical Quality Control - Tan, Steinbach, and Kumar (2006), Introduction to Data Mining - Tsiptsis and Chorianopoulos (2009), Data Mining Techniques in CRM |
